
🧬 LangGraph实战项目:从零复现DeepResearch自动化研究代理
本文是 《LangGraph入门全解》https://www.wileyzhang.com/posts/264605ee-e889-806e-b847-ce4e7bcba614 系列的第六篇,也是最后一篇。今年Agent爆发,Gemini,ChatGPT等都推出了自己的深度研究功能,本篇我们使用LangGraph复现DeepResearch,也许完成度没那么高,但是功能是全的。如果出你是新手,建议先阅读主指南以了解LangGraph的全貌。
LangGraph实现DeepResearch
我们在使用AI问答的过程中,AI的答案往往只依赖模型已有的训练数据,或者仅仅做一次搜索。这种方式虽然快速,但结果往往不够全面,还可能被单一上下文影响,导致结论片面。
回想我们在写毕业论文时的流程: 确定研究问题 → 查阅多篇文献 → 做笔记 → 比对分析 → 形成观点 → 引用参考文献。
而 DeepResearch 的核心思想,正是模仿人类这种系统化的调研方式。它利用 链式思维(Chain-of-Thought)和反思性推理(Reflective Reasoning),一步步推进研究过程,直到得到足够可靠的答案。
DeepResearch流程图
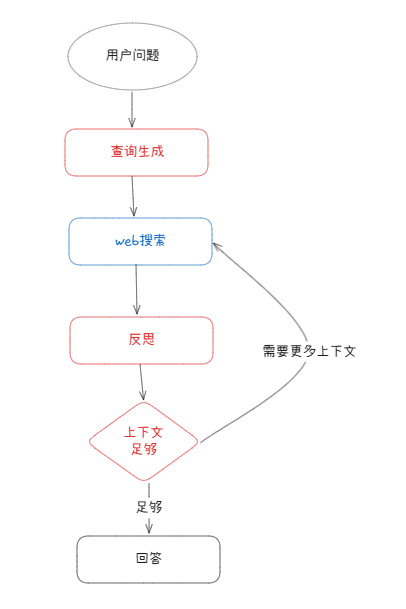
- 生成初始查询:根据用户输入,模型会生成一组搜索查询。
- 网络研究:针对每个查询,通过模型和搜索工具查找相关网页。
- 反思与差距分析:代理对搜索结果进行分析,判断信息是否足够,是否存在知识盲点。
- 迭代细化:如果发现不足,自动生成后续查询,重复“搜索—反思”的循环(直到达到设定的最大次数)。
- 生成最终答案:当研究内容足够时,模型整合信息,生成一个逻辑清晰、带引用的最终答案。
代码示例
在实现过程中,我将整个 Agent 拆分为三个文件:
prompts.py:定义所有提示词(Prompt)state_schema.py:定义状态与结构化输出的 Schemagraph.py:定义 Agent 的执行逻辑
配置必要的环境变量
export TAVILY_API_KEY="" export OPENAI_API_KEY="" export OPENAI_BASE_URL=""
prompt.py
from datetime import datetime def get_current_date(): # 获取当前日期函数 return datetime.now().strftime("%B %d, %Y") query_writer_instructions = """您的目标是生成复杂且多样化的网络搜索查询。这些查询适用于能够分析复杂结果、跟踪链接和综合信息的高级自动化网络研究工具。 指示: - 始终首选单个搜索查询,仅当原始问题要求多个方面或元素并且一个查询不够时才添加另一个查询。 - 每个查询都应关注原始问题的一个特定方面。 - 不要生成超过5个查询。 - 查询应该是多样化的,如果主题很广泛,则生成 1 个以上的查询。 - 不要生成多个类似的查询,1 个就足够了。 - 查询应确保收集最新信息。当前日期为 {current_date}。 格式: - 使用以下两个确切键将响应格式化为 JSON 对象: - “rationale”:简要解释为什么这些查询是相关的 - “query”:搜索查询列表 示例: 主题:去年哪些收入增长更多 苹果股票或购买 iPhone 的人数 json {{ “rationale”: “为了准确回答这个比较增长问题,我们需要有关苹果股票表现和 iPhone 销售指标的具体数据点。这些查询针对所需的精确财务信息:公司收入趋势、特定产品的单位销售数据以及同一财政期间的股价变动,以便直接比较。 “query”: [“苹果2024财年总收入增长”、“2024财年iPhone销量增长”、“2024财年苹果股价增长”], }} 上下文:{research_topic}""" web_searcher_prompt = """进行有针对性的搜索,收集有关“{research_topic}”的最新、可信的信息,并将其合成为可验证的文本。 指示: - 查询应确保收集最新信息。当前日期为 {current_date}。 - 进行多种不同的搜索以收集全面的信息。 - 整合关键发现,同时仔细跟踪每个特定信息的来源。 - 输出应该是根据您的搜索结果编写良好的摘要或报告。 - 只包含搜索结果中发现的信息,不要编造任何信息。 研究课题: {research_topic} """ reflection_instructions = """您是一名专家研究助理,分析有关“{research_topic}”的摘要。 指示: - 识别知识差距或需要深入探索的领域并生成后续查询。(1 或多个)。 - 如果提供的摘要足以回答用户的问题,请不要生成后续查询。 - 如果存在知识差距,请生成有助于扩展您的理解的后续查询。 - 关注未完全涵盖的技术细节、实施细节或新兴趋势。 要求: - 确保后续查询是独立的,并包含网络搜索的必要上下文。 输出格式: - 使用以下确切键将响应格式化为 JSON 对象: - “is_sufficient”:true or false - “knowledge_gap”:描述哪些信息缺失或需要澄清 - “follow_up_queries”:写一个具体的问题来解决这一差距 示例: json {{ “is_sufficient”: true, // 或 false “knowledge_gap”: “摘要缺少有关性能指标和基准的信息”, // “如果is_sufficient为 true, “follow_up_queries”: [“用于评估 [特定技术] 的典型性能基准和指标是什么?”] // [](如果is_sufficient为 true) }} 仔细反思摘要,以确定知识差距并生成后续查询。然后,按照以下 JSON 格式生成输出: 摘要: {summaries} """ answer_instructions = """根据提供的摘要为用户的问题生成高质量的答案。 指示: - 当前日期是 {current_date}。 - 你是多步骤研究过程的最后一步,不要说你是最后一步。 - 您可以访问从前面的步骤中收集的所有信息。 - 您可以访问用户的问题。 - 根据提供的摘要和用户的问题,为用户的问题生成高质量的答案。 - 使用MarkDown编写答案。这是必须的。 用户上下文: - {research_topic} 摘要: {summaries} """
state_schema.py
from __future__ import annotations from dataclasses import dataclass, field from typing import TypedDict, List from typing_extensions import Annotated import operator from pydantic import BaseModel, Field class SearchQueryList(BaseModel): query: List[str] = Field( description="用于 Web 研究的搜索查询列表。" ) rationale: str = Field( description="简要解释为什么这些查询与研究主题相关。" ) class Reflection(BaseModel): is_sufficient: bool = Field( description="提供的摘要是否足以回答用户的问题。" ) knowledge_gap: str = Field( description="对缺少或需要澄清的信息的描述。" ) follow_up_queries: List[str] = Field( description="解决知识差距的后续查询列表。" ) class OverallState(TypedDict): topic: str # 研究主题 search_query: Annotated[list, operator.add] # 搜索列表 web_research_result: Annotated[list, operator.add] # 搜索摘要结果 research_loop_count: int # 当前循环次数 max_research_loops: int # 最大循环次数 is_sufficient: bool # 是否足够研究 knowledge_gap: str # 当前搜索后,还缺少的信息 follow_up_queries: List[str] # 接下来需要搜索的问题 final_answer: str class ReflectionState(TypedDict): is_sufficient: bool knowledge_gap: str follow_up_queries: List[str] research_loop_count: int number_of_ran_queries: int class Query(TypedDict): query: str rationale: str class QueryGenerationState(TypedDict): search_query: list[Query] class WebSearchState(TypedDict): search_query: str
graph.py
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI from langchain_tavily import TavilySearch from langgraph.types import Send from langgraph.graph import StateGraph from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent from langgraph.graph import START, END from state_schema import SearchQueryList, Reflection, OverallState,QueryGenerationState,ReflectionState,WebSearchState from prompts import get_current_date,query_writer_instructions,reflection_instructions,answer_instructions,web_searcher_prompt # 此处定义你自己的模型 llm = ChatOpenAI(model="qwen3_32") # 此处定义搜索工具 tool = TavilySearch(max_results=2) # Nodes def generate_query(state: OverallState) -> QueryGenerationState: """分解用户问题"""structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(SearchQueryList) current_date = get_current_date() formatted_prompt = query_writer_instructions.format( current_date=current_date, research_topic=state["topic"] ) result = structured_llm.invoke(formatted_prompt) return {"search_query": result.query} def continue_to_web_research(state: OverallState): """ """return [ Send("web_research", {"search_query": search_query}) for idx, search_query in enumerate(state["search_query"]) ] def web_research(state: WebSearchState) -> OverallState: """创建一个搜索Agent"""formatted_prompt = web_searcher_prompt.format( current_date=get_current_date(), research_topic=state["search_query"], ) agent = create_react_agent(model=llm,tools=[tool],) response = agent.invoke({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": formatted_prompt}]}) return {"web_research_result": [response["messages"][-1].content]} def reflection(state: OverallState) -> ReflectionState: """反思节点,分析摘要内容,并确定是否需要进一步搜索"""state["research_loop_count"] = state.get("research_loop_count", 0) + 1 current_date = get_current_date() formatted_prompt = reflection_instructions.format( current_date=current_date, research_topic=state["topic"], summaries="\n\n---\n\n".join(state["web_research_result"]), ) result = llm.with_structured_output(Reflection).invoke(formatted_prompt) return { "is_sufficient": result.is_sufficient, "knowledge_gap": result.knowledge_gap, "follow_up_queries": result.follow_up_queries, "research_loop_count": state["research_loop_count"], "number_of_ran_queries": len(state["search_query"]), } def evaluate_research( state: OverallState, ) -> OverallState: """路由函数,非节点"""max_research_loops = state.get("max_research_loops") if state["is_sufficient"] or state["research_loop_count"] >= max_research_loops: return "finalize_answer" else: return [ Send("web_research",{"search_query": follow_up_query,},) for idx, follow_up_query in enumerate(state["follow_up_queries"]) ] def finalize_answer(state: OverallState): """生成最终回答""" current_date = get_current_date() formatted_prompt = answer_instructions.format( current_date=current_date, research_topic=state["topic"], summaries="\n---\n\n".join(state["web_research_result"]), ) result = llm.invoke(formatted_prompt) return {"final_answer": result.content,} grpah = StateGraph(OverallState) grpah.add_node("generate_query", generate_query) grpah.add_node("web_research", web_research) grpah.add_node("reflection", reflection) grpah.add_node("finalize_answer", finalize_answer) grpah.add_edge(START, "generate_query") grpah.add_conditional_edges( "generate_query", continue_to_web_research, ["web_research"] ) grpah.add_edge("web_research", "reflection") grpah.add_conditional_edges( "reflection", evaluate_research, ["web_research", "finalize_answer"] ) grpah.add_edge("finalize_answer", END) app = grpah.compile()
监控与调试
官方的LangSmith用于监控Agent的执行非常的方便。
但是数据会上传到Langchain服务器,不建议在敏感项目中使用。
-
申请API Key,登录LangSmith https://smith.langchain.com%EF%BC%8C%E5%85%8D%E8%B4%B9%E8%8E%B7%E5%8F%96Key
-
安装LangGraph-cli
pip install --upgrade "langgraph-cli[inmem]" -
创建配置文件
langgraph.json,内容如下。按照实际情况修改配置,如有问题,评论区联系{ "dependencies": ["."], "graphs": { "agent": "graph:app" }, "env": ".env", "image_distro": "wolfi" } -
创建环境变量文件
.env,写入第一步申请的KeyLANGSMITH_API_KEY=lsv2_pt_xxxxxxx -
使用命令
langgraph dev启动,复制图中链接到浏览器中打开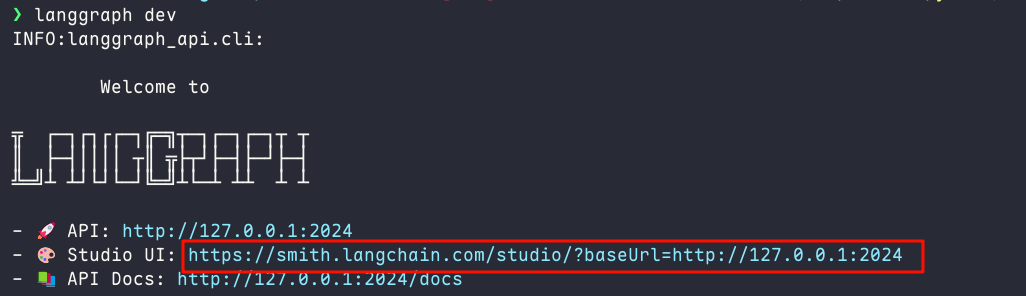
-
查看Graph并执行,写入研究主题,最大循环次数,提交
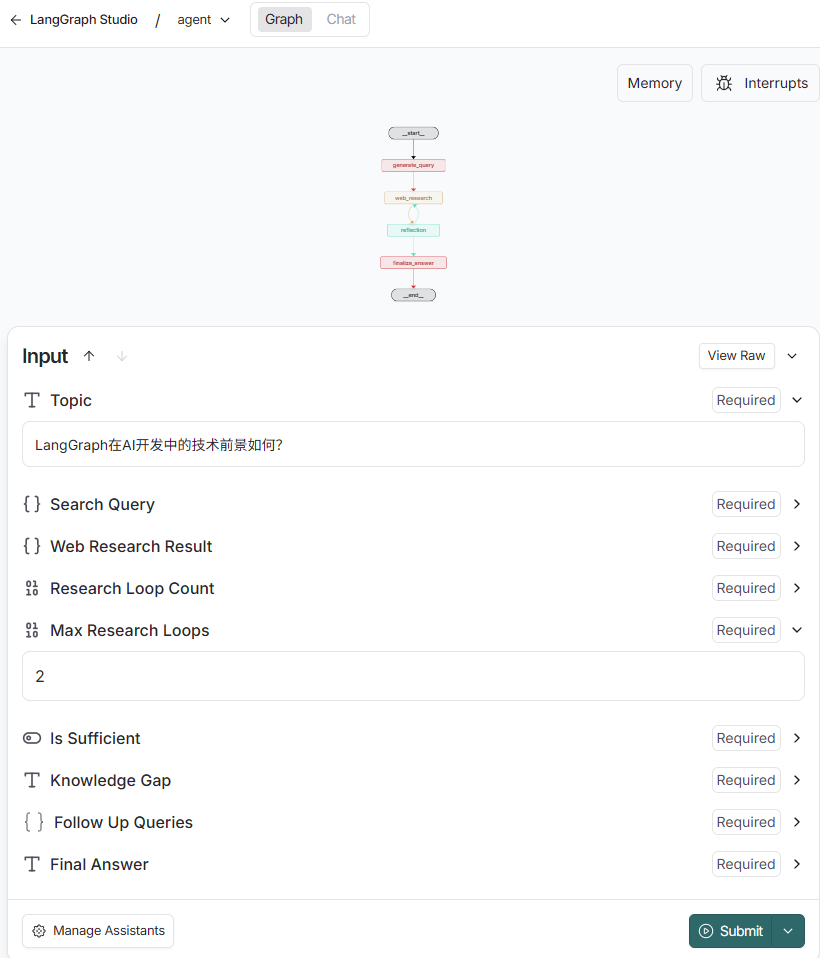
-
Agent开始运行,可以在右侧的界面上看到每一步执行的情况,整个流程运行了约5分钟。
